Cells & Oxygen Availability | Nobel Special
TAPP Radio Episode 54 Bonus
Quick Take
Host Kevin Patton summarizes the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to three scientists “for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.” A special bonus episode.
00:41 | Introduction to Bonus Episode
02:00 | Sponsored by HAPS
02:24 | Summary of Discovery
04:13 | Oxygen at Center Stage
05:24 | HIF Enters the Scene
08:08 | Sponsored by AAA
08:26 | VHL – An Unexpected Partner
11:37 | Oxygen sHIFts the Balance
13:20 | Oxygen Shapes Physiology & Pathology
15:15 | Sponsored by HAPI Online Graduate Program
15:48 | Our Course
23:46 | Staying Connected
Listen Now!
Singing is like a celebration of oxygen. (Björk)
1 | Introduction to the Bonus Episode
1 minute
Kevin introduces the bonus episode, explaining that he’s sharing the press release for the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. It’s chunked for clarity.
Press release: The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019. NobelPrize.org. Nobel Media AB 2019. Mon. 7 Oct 2019. <https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2019/press-release/>
2 | Sponsored by HAPS
2 minutes
 The Human Anatomy & Physiology Society (HAPS) is a sponsor of this podcast. You can help appreciate their support by clicking the link below and checking out the many resources and benefits found there. There are a bunch of 1-day regional workshops scattered all over the continent. There’s probably one near you coming up this year (or next)!
The Human Anatomy & Physiology Society (HAPS) is a sponsor of this podcast. You can help appreciate their support by clicking the link below and checking out the many resources and benefits found there. There are a bunch of 1-day regional workshops scattered all over the continent. There’s probably one near you coming up this year (or next)!
3 | Summary of the Discovery
2 minutes
- 2019-10-07: The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly to William G. Kaelin Jr., Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, and Gregg L. Semenza for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.
- They identified molecular machinery that regulates the activity of genes in response to varying levels of oxygen.
4 | Oxygen at Center Stage
1 minute
During evolution, mechanisms developed to ensure a sufficient supply of oxygen to tissues and cells.
5 | HIF Enters the Scene
3 minutes
- Gregg Semenza studied the EPO (erythropoietin) gene and how it is regulated by varying oxygen levels.
- In cultured liver cells he discovered a protein complex that binds to the identified DNA segment in an oxygen-dependent manner. He called this complex the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF).
- HIF was found to consist of two different DNA-binding proteins, so called transcription factors, now named HIF-1α and ARNT.
6 | Sponsored by AAA
0.5 minutes
- A searchable transcript for this episode, as well as the captioned audiogram of this episode, are sponsored by the American Association for Anatomy (AAA) at anatomy.org.
7 | VHL – An Unexpected Partner
3 minutes
- When oxygen levels are high, cells contain very little HIF-1α. However, when oxygen levels are low, the amount of HIF-1α increases so that it can bind to and thus regulate the EPO gene as well as other genes with HIF-binding DNA segments.
- See figure (if you can’t see it, go to https://my-ap.us/35fm0O6).
- At about the same time as Semenza and Ratcliffe were exploring the regulation of the EPO gene, cancer researcher William Kaelin, Jr. was researching an inherited syndrome, von Hippel-Lindau’s disease (VHL disease).
- VHL is part of a complex that labels proteins with ubiquitin, marking them for degradation in the proteasome.
- Ratcliffe and his research group then made a key discovery: demonstrating that VHL can physically interact with HIF-1α and is required for its degradation at normal oxygen levels. This conclusively linked VHL to HIF-1α.
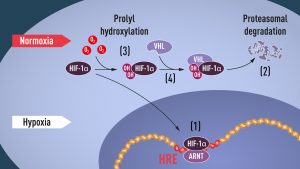
When oxygen levels are low (hypoxia), HIF-1α is protected from degradation and accumulates in the nucleus, where it associates with ARNT and binds to specific DNA sequences (HRE) in hypoxia-regulated genes (1). At normal oxygen levels, HIF-1α is rapidly degraded by the proteasome (2). Oxygen regulates the degradation process by the addition of hydroxyl groups (OH) to HIF-1α (3). The VHL protein can then recognize and form a complex with HIF-1α leading to its degradation in an oxygen-dependent manner (4). https://my-ap.us/35fm0O6
8 | Oxygen sHIFts the Balance
1.5 minutes
- It was also shown that the gene activating function of HIF-1α was regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation.
- The Nobel Laureates had now elucidated the oxygen sensing mechanism and had shown how it works.
9 | Oxygen Shapes Physiology & Pathology
2 minutes
- Thanks to the groundbreaking work of these Nobel Laureates, we know much more about how different oxygen levels regulate fundamental physiological processes.
- For example, muscles, blood vessel formation, immunity, RBC production, placenta development, etc.
- Oxygen sensing is central to a large number of diseases.
- For example, patients with chronic renal failure often suffer from severe anemia due to decreased EPO expression. See figure (if you cant’s see it, go to https://my-ap.us/2LW2cIb)
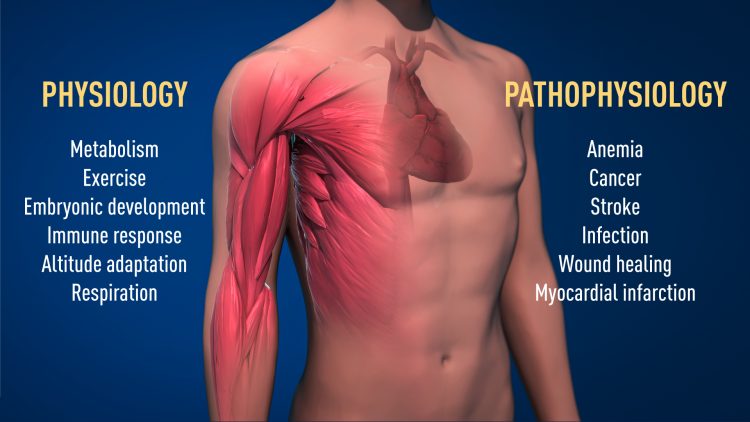
The awarded mechanism for oxygen sensing has fundamental importance in physiology, for example for our metabolism, immune response and ability to adapt to exercise. Many pathological processes are also affected. Intensive efforts are ongoing to develop new drugs that can either inhibit or activate the oxygen-regulated machinery for treatment of anemia, cancer and other diseases. https://my-ap.us/2LW2cIb
10 | Sponsored by HAPI Online Graduate Program
1 minute
 The Master of Science in Human Anatomy & Physiology Instruction—the MS-HAPI—is a graduate program for A&P teachers. A combination of science courses (enough to qualify you to teach at the college level) and courses in contemporary instructional practice, this program helps you power up your teaching. Kevin Patton is a faculty member in this program. Check it out!
The Master of Science in Human Anatomy & Physiology Instruction—the MS-HAPI—is a graduate program for A&P teachers. A combination of science courses (enough to qualify you to teach at the college level) and courses in contemporary instructional practice, this program helps you power up your teaching. Kevin Patton is a faculty member in this program. Check it out!
11 | Our Course
8 minutes
- This set of discoveries touches on many of the core concepts of our course (the big ideas of our story of the human body).
- Nobel Prizes are a cultural touchstone that students can related to, and thus increase interest and motivation.
- Nobel Prizes can be a starting point for discussion the role of science in the context of society and culture.
- Additional resources:
- Main page for this prize: my-ap.us/31Wuc3Z
- Publications
- Semenza, G.L, Nejfelt, M.K., Chi, S.M. & Antonarakis, S.E. (1991). Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3’ to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 88, 5680-5684 my-ap.us/2ontmP8
- Wang, G.L., Jiang, B.-H., Rue, E.A. & Semenza, G.L. (1995). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92, 5510-5514 my-ap.us/2IxLUD5
- Maxwell, P.H., Wiesener, M.S., Chang, G.-W., Clifford, S.C., Vaux, E.C., Cockman, M.E., Wykoff, C.C., Pugh, C.W., Maher, E.R. & Ratcliffe, P.J. (1999). The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature, 399, 271-275 my-ap.us/2op4XbP
- Mircea, I., Kondo, K., Yang, H., Kim, W., Valiando, J., Ohh, M., Salic, A., Asara, J.M., Lane, W.S. & Kaelin Jr., W.G. (2001) HIFa targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implications for O2 sensing. Science, 292, 464-468 my-ap.us/2IxIf8t
- Jakkola, P., Mole, D.R., Tian, Y.-M., Wilson, M.I., Gielbert, J., Gaskell, S.J., von Kriegsheim, A., Heberstreit, H.F., Mukherji, M., Schofield, C.J., Maxwell, P.H., Pugh, C.W. & Ratcliffe, P.J. (2001). Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science, 292, 468-472 my-ap.us/35i4wR9
Need help accessing resources locked behind a paywall?
Check out this advice from Episode 32 to get what you need!
(If no link or player are visible, go to https://youtu.be/JU_l76JGwVw?t=440)
This podcast is sponsored by the
Human Anatomy & Physiology Society

This podcast is sponsored by the
Master of Science in
Human Anatomy & Physiology Instruction

Stay Connected
The easiest way to keep up with new episodes is with the free mobile app:
Or you can listen in your favorite podcast or radio app.
Click here to be notified by blog post when new episodes become available (make sure The A&P Professor option is checked).
Transcript
To read a complete transcript of this episode,
click here.
The searchable transcript for this episode is sponsored by
The American Association for Anatomy.
Call in
Record your question or share an idea and I may use it in a future podcast!
Toll-free:
1·833·LION·DEN
(1·833·546·6336)
Local:
1·636·486·4185
Email:
podcast@theAPprofessor.org
Share
![]() Please click the orange share button at the bottom left corner of the screen to share this page!
Please click the orange share button at the bottom left corner of the screen to share this page!
Last updated: October 23, 2019 at 23:46 pm





